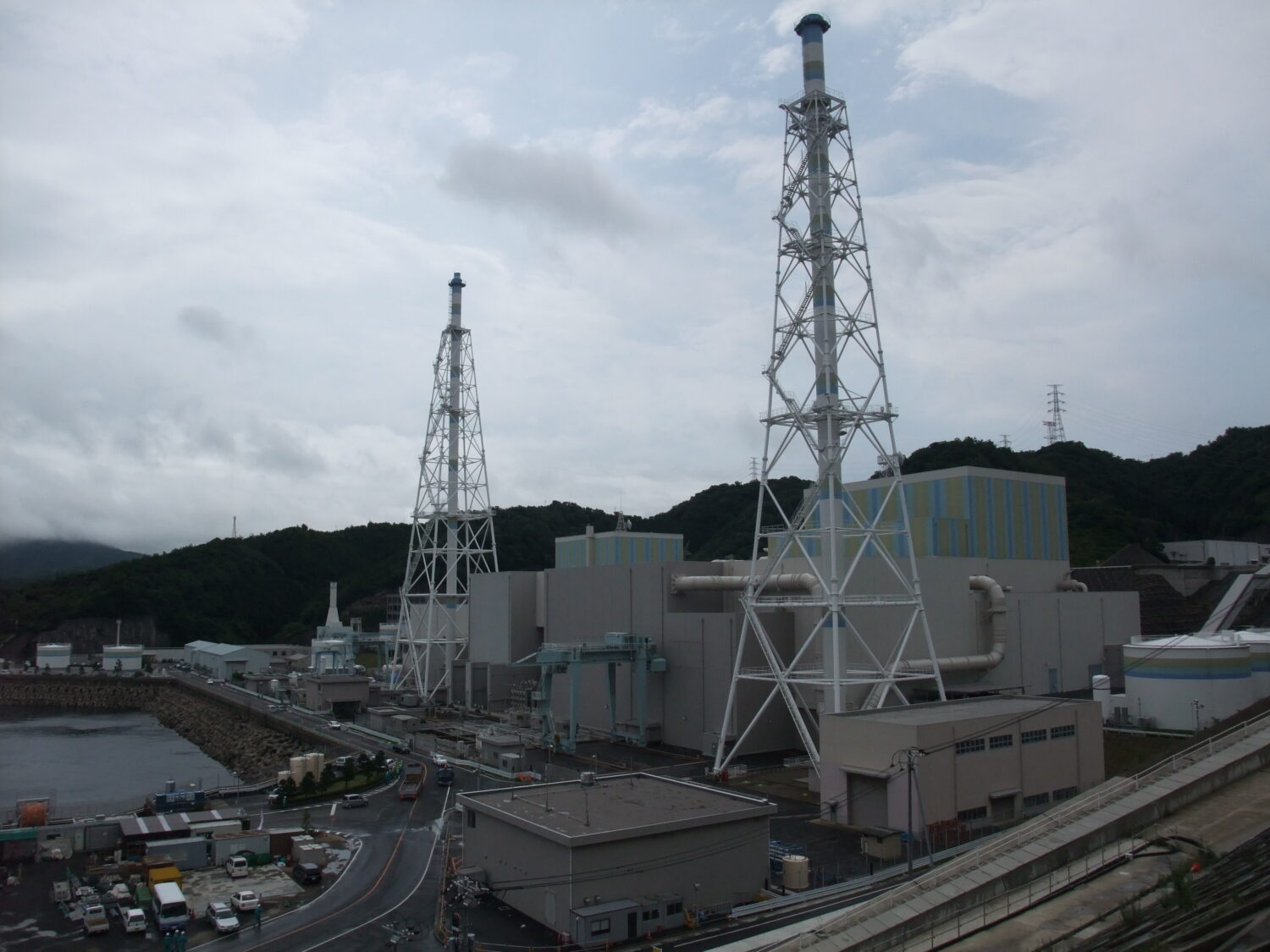
In 2016, based on examinations by the Nuclear Regulation Authority of Japan (NRA) to confirm the compatibility of the three units with the new regulatory standards, the power utility was granted approval to make changes to the reactor installations (basic design approval) and to extend their operating lifetimes to sixty years.
Kansai EP has been carrying out activities to implement safety and disaster measures and to obtain local understanding. On April 28, the governor of Fukui Prefecture expressed his agreement to restarting the reactors.
At the Mihama-3, fuel will start being loaded on May 20, and the reactor will be restarted and will resume generation in late June. The following month, after a period of adjustment operations, Mihama-3 is expected to return to full service after a decade. It will be the first NPP in Japan to operate beyond forty years.
Thereafter, however, the operation of Mihama-3 will be suspended again before the expected restart, since the facilities have not been completed for responding to specific severe accidents—termed “specific safety facilities”—which are required under the new regulatory standards as anti-terrorism measures. The deadline for completing those facilities is October 25, and their design and (initial) work plans were only approved by the NRA in April.
Fuel began to be loaded at the Takahama-1 on May 14. During the loading, Kansai EP will conduct related inspections to confirm the soundness of facilities and equipment. The Takahama-2, meanwhile, is now undergoing work on safety improvement measures.
However, since the deadlines for the “specific safety facilities” are imminent for both units (namely, June 9), no times have been shown for their restart. They will only be restarted once the required work is completed.



-1.png)