With the aim of reversing the negative consequences of Covid-19 and turn them into societal opportunities that help realize a future infused with hope, the New Capitalism Implementation Council, composed of experts, started work the same month.
Representing supply chain industries, MIMURA Akio, who was then president of the Japan Chamber of Commerce and Industry (JCCI) and is currently chairman of the Japan Atomic Industrial Forum (JAIF), participated in the council as one of its initial members.
The action plan in the current revision (its second) includes the following six points:
- Giving wage increases to workers at small- and medium-size enterprises.
- Implementing integrated, three-pronged labor market reforms at an early date.
- Reforming industry to facilitate the smooth entry and exit of corporations.
- Promoting domestic investments.
- Achieving GX, energy security, and food security.
- Promoting Japan as a leading asset management center.
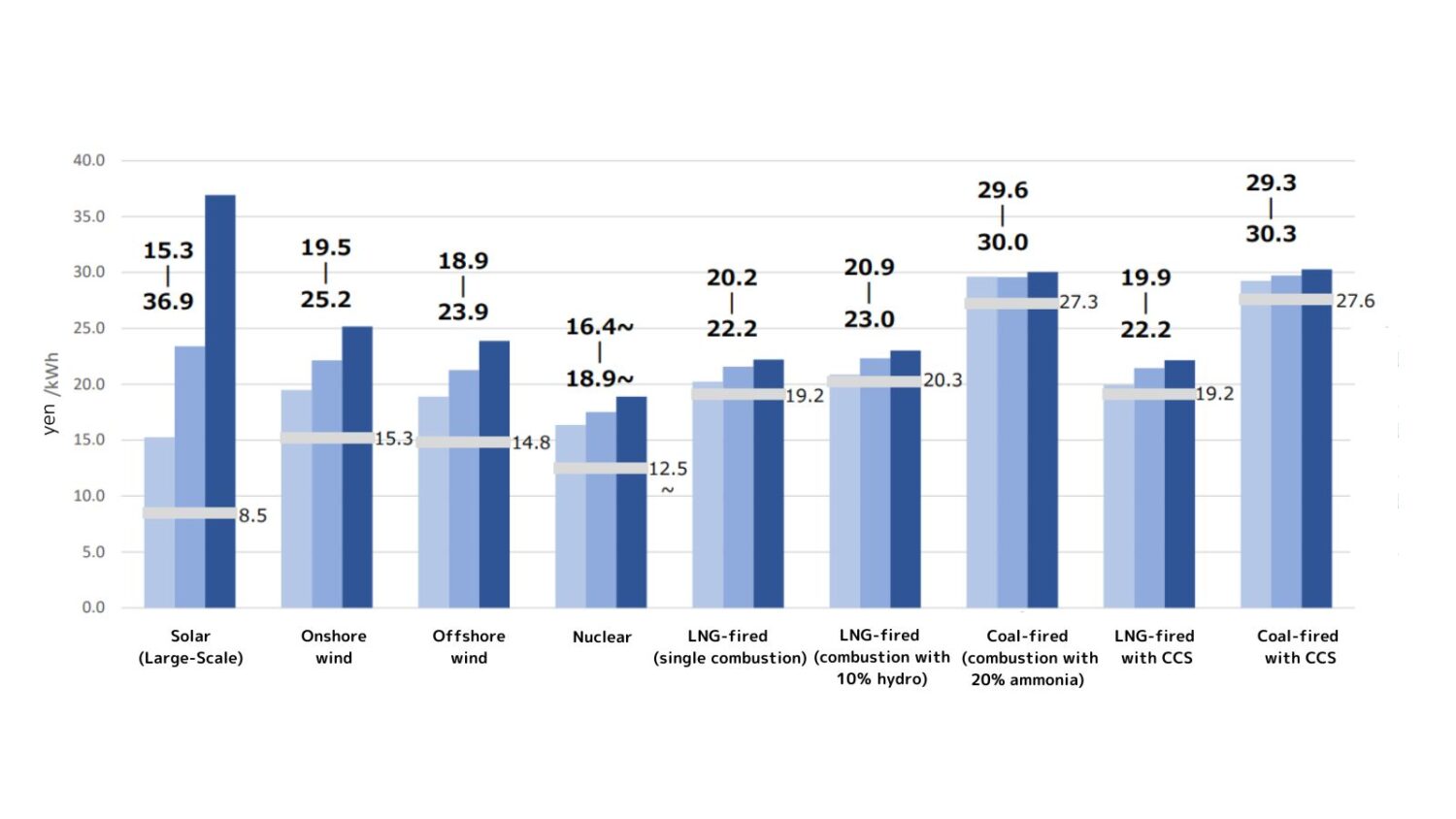
Insofar as GX and energy are concerned, the plan stressed the importance of stable, robust energy, stating that “the current situation—wherein huge amounts of money, on the order of several trillion yen, flow out of the country because of energy imports—must be changed.” Adding that “the issuance and implementation of a national strategy is essential to shift the current energy structure toward one that leads to decarbonization and contributes to strengthening competitiveness,” the council said that it aims to intensively discuss revisions to the Strategic Energy Plan during the current fiscal year (which ends on March 31, 2025).
It then stated that a GX National Strategy would be carried out to further promote the Strategy for Promoting the Transition to a Decarbonized Growth-Oriented Economic Structure (GX Promotion Strategy), issued in 2023.
Turning to the topic of nuclear energy use, the plan will promote the restart of nuclear power plants (NPPs), based on ensured safety and the confirmation of compatibility with the new regulatory standards by the Nuclear Regulation Agency (NRA) through its examinations and inspections, for which understanding had been obtained from local communities.
It also stated that Japan would endeavor to develop and build next-generation NPPs, including fast reactors, high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), and fusion reactors.